What's the advantages of wireless Lighting technology?
Wireless lighting refers to lighting systems that use wireless communication technology for control and management and lighting systems are connected to wireless gateways through wireless communication modules, and wireless gateways communicate with mobile phone apps through Wi-Fi or Bluetooth technology. These systems usually include components such as lamps, wireless gateways, and mobile phone apps. The basic principle of intelligent lighting systems is to use various sensors to capture environmental information (such as light, traffic, etc.), and automatically adjust parameters such as light brightness, color, and irradiation direction according to preset programs or user needs to achieve energy saving and improve comfort.
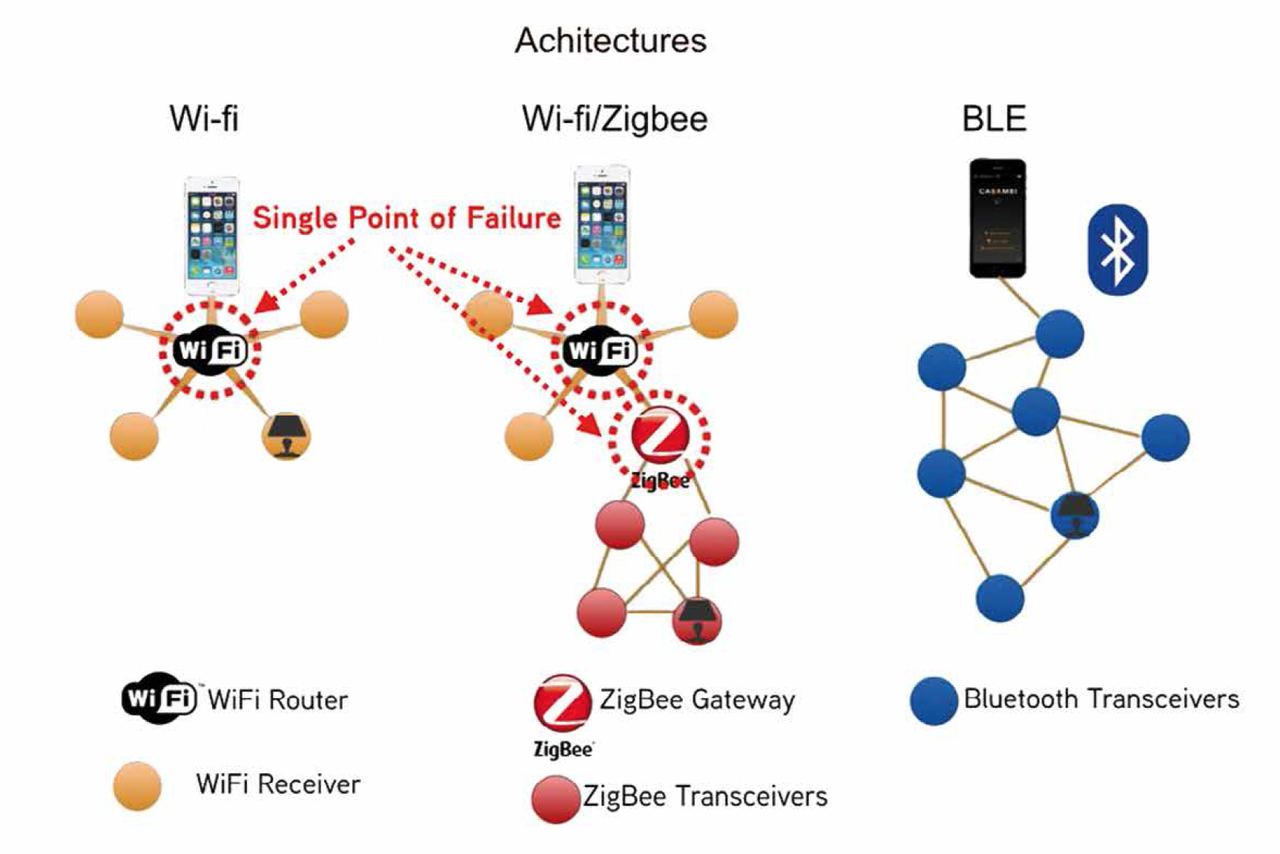
A variety of wireless communication protocols have been developed to enable the transmission of commands from control devices to LED lights, each with unique advantages and use cases:
Wi-Fi
Wi-Fi is a popular protocol for in-home wireless lighting due to its compatibility with many smart home systems and its ability to transmit data over relatively long distances. Wi-Fi-enabled lights can be controlled virtually anywhere via the internet, allowing remote adjustments when users are away. However, Wi-Fi’s power consumption is generally higher than that of other protocols, making it more suitable for installations with constant power sources.
Bluetooth
Bluetooth technology is commonly used in wireless LED systems due to its low power consumption and ease of integration. Bluetooth-enabled lights are typically controlled via a nearby mobile device, offering a reliable solution within short distances (around 10–30 meters). The introduction of Bluetooth Mesh has further enhanced the protocol’s capabilities, enabling larger, interconnected networks of lights ideal for residential and small commercial applications.
Zigbee
Zigbee is a low-power, short-range wireless protocol optimized for communication between a network of devices. Zigbee-enabled lights are typically part of a mesh network, where each light acts as a repeater, extending the network’s range and reliability. This protocol is commonly used in intelligent lighting systems for residential and commercial spaces due to its power efficiency and ability to handle many devices within the same network.
Z-Wave
Similar to Zigbee, Z-Wave is designed specifically for home automation. It operates on a low-frequency band that minimizes interference from Wi-Fi networks. Z-Wave is highly compatible with many smart home hubs, making it an attractive choice for interconnected home lighting systems. Its range extends further than Bluetooth but typically requires a central hub for communication, making it ideal for residential applications where connectivity and ease of use are top priorities.
Together, these protocols play a pivotal role in making wireless LED systems responsive, versatile, and energy-efficient, providing users with a broad range of options to suit different environments and preferences. The rise of wireless communication in lighting has made it possible to create highly customizable, integrated systems that elevate lighting from a functional necessity to a feature that enhances the overall user experience.




Wireless LED lighting has revolutionized how we illuminate various environments by offering convenience, control, and adaptability across numerous applications. This flexibility makes wireless LED lighting an attractive choice in settings that range from residential and commercial spaces to outdoor and public environments. Here is a detailed look at some of the most impactful applications of wireless LED lighting.
3.1 Residential Applications
Wireless LED lighting has become a cornerstone of smart living in the modern home. Wireless systems allow homeowners to remotely control lights through smartphone apps or voice-controlled smart assistants such as Amazon Alexa, Google Assistant, or Apple's Siri. This allows users to set timers, adjust brightness, change colors, or schedule different light scenes throughout the day. For example, you can set dim lights in the evening to promote relaxation and bright lights in the morning to promote productivity.
Wireless lighting is also beneficial in home security, as users can control lights while away, creating the impression of occupancy. Motion sensors integrated into wireless systems add an extra layer of protection by illuminating pathways or alerting homeowners of movement. Additionally, with wireless LED lighting, indoor and outdoor lights can easily be added without complicated wiring, making it ideal for renovations or new installations.
3.2 Commercial and Retail Spaces
Wireless LED lighting has a transformative impact in commercial and retail spaces, where ambiance, branding, and customer experience are paramount. Retail stores, for instance, can adjust lighting colors and intensities to match seasonal promotions, highlight new products, or create unique atmospheres tailored to the shopping experience. The ability to wirelessly control lights also allows stores to manage lighting in multiple locations from a central hub, saving labor and energy costs.
3.3 Outdoor and Landscape Lighting
Wireless LED lighting is ideal for outdoor applications, offering a reliable and aesthetically pleasing option for illuminating gardens, pathways, architectural features, and public spaces. For homeowners and landscape designers, wireless LED lighting provides flexibility in positioning fixtures, eliminating the need for extensive wiring that can disrupt landscapes. Outdoor wireless lighting is often equipped with solar panels and motion sensors to save energy and provide security, activating only when movement is detected.
3.4 Wireless lighting systems benefit public spaces
Like parks, plazas, and pedestrian walkways by offering remote control, monitoring, and scheduling capabilities. Municipalities can adjust lighting levels in response to crowd presence, time of day, or energy-saving initiatives. Wireless systems also streamline maintenance; managers can remotely identify and address faults, reducing downtime and ensuring public spaces remain well-lit and safe.
3.5 Industrial and Warehouse Settings
Wireless LED lighting is increasingly popular in industrial environments, such as factories, warehouses, and distribution centers, where traditional wiring can be impractical due to high ceilings and complex layouts. Wireless lighting allows facilities to manage lights efficiently, grouping them by area or activity type and adjusting them in response to changes in occupancy or ambient light levels. Motion sensors can optimize lighting by illuminating areas only when used, reducing energy consumption in unoccupied zones.
Wireless LED lighting improves safety and productivity in warehouses by ensuring that work areas are adequately lit without causing unnecessary glare or energy waste. Facilities managers can also monitor lighting status across vast spaces from a central control panel, simplifying maintenance and allowing for faster response times if any lighting issues arise.
Wireless technology plays a pivotal role in smart buildings, but it should be viewed as a complement to, rather than a replacement for, wired infrastructure. The allure of wireless is undeniable – it offers flexibility, mobility and ease of installation that wired networks can seldom match. This makes it ideal for areas where wiring is impractical or for devices that need to be mobile or reconfigured frequently.
However, the inherent limitations of wireless technology must be acknowledged. Wireless networks are more susceptible to interference, which can impact reliability, particularly in environments with a high density of devices or physical obstructions. Additionally, while advances in wireless technology have significantly improved its speed and bandwidth capabilities, it still generally falls short of the high-speed, high-capacity performance offered by wired connections.
In the context of smart building design and IoT integration, then, wireless technology should not be seen as an all-encompassing solution, but rather as a valuable component of a broader, hybrid network strategy. This approach aligns well with the principles of modern local area network (LAN) design, where flexibility, security and efficiency are paramount.
Wired Systems for Stability: In environments where reliability and consistency are paramount—such as industrial facilities or emergency lighting—wired systems may remain the preferred choice.
Wireless Systems for Flexibility: Wireless systems offer unparalleled advantages for applications that demand adaptability, scalability, and ease of installation.
This coexistence reflects the diverse lighting requirements across various sectors, ensuring that both technologies continue to evolve and complement each other.
Wireless LED lighting is undoubtedly a significant force shaping the future of illumination. With its blend of intelligent functionality, energy efficiency, and design flexibility, it addresses the needs of modern living and aligns with global trends in technology and sustainability. However, challenges like network security, costs, and technical limitations must be addressed to unlock its full potential.
A harmonious integration of wired and wireless technologies in smart building infrastructure is essential. Embracing the strengths of both, rather than choosing one over the other, offers a more comprehensive, secure and sustainable approach to building networks. This strategy not only caters to the current demands of IoT and smart technologies but also positions these infrastructures to adapt and evolve with future developments.

Shenzhen Yuanyeled Co.,Ltd. is a professional company, was established in 2011 based in Shenzhen, China with over 10-year experience in LED lighting industry starting with LED encapsulation.
CONTACT US
Email: rice@yuanyeled.com
Tel: +86-19925346944
WhatsApp: +86-19925346944
ADD: Floor 8th, building 8, Langxia third industrial zone, Songgang town, Baoan district, Shenzhen city, China.